策略模式
举例:
- 比较器
- 旅行路线
- 固定算法策略(封装)
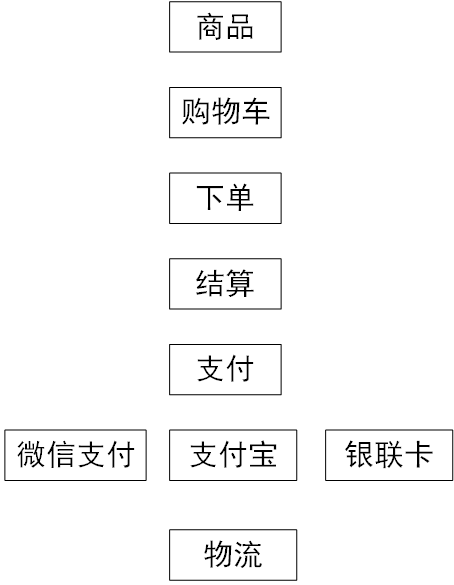
- 买东西结算支付
场景:
根据用户的需求处理数据时候需要对算法做出选择,固定的一些算法(不再发生变化的算法),扩展。(算法会变的时候,不建议用策略模式)
客户本身就知道要采用什么样的算法去计算。(有选择的权利)
==assets/支付的策略模式.png==
策略模式代码:
Order.class
java
public class Order {
private String uId;
private String orderId;
private double amount;
public Order(String uId, String orderId, double amount) {
this.uId = uId;
this.orderId = orderId;
this.amount = amount;
}
// public PayState pay(Payment payment) {
// return payment.pay(this.uId,this.amount);
// }
// 这个参数,完全可以用 Payment 这个接口来代替
// 为什么?
// 完美地解决了 switch 的过程, 不需要在代码逻辑中写 switch le
// 更不需要写 if else 了
public PayState pay(PayType payType) {
return payType.getPayment().pay(this.uId, this.amount);
}
}public class Order {
private String uId;
private String orderId;
private double amount;
public Order(String uId, String orderId, double amount) {
this.uId = uId;
this.orderId = orderId;
this.amount = amount;
}
// public PayState pay(Payment payment) {
// return payment.pay(this.uId,this.amount);
// }
// 这个参数,完全可以用 Payment 这个接口来代替
// 为什么?
// 完美地解决了 switch 的过程, 不需要在代码逻辑中写 switch le
// 更不需要写 if else 了
public PayState pay(PayType payType) {
return payType.getPayment().pay(this.uId, this.amount);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
PayState.class
java
/**
* 支付完成以后的状态
**/
public class PayState {
private int code;
private String msg;
private Object data;
public PayState(int code, String msg, Object data) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PayState{" +
"[交易状态:]code=" + code +
", [交易详情:]data=" + data +
", msg='" + msg + '\'' +
'}';
}
}/**
* 支付完成以后的状态
**/
public class PayState {
private int code;
private String msg;
private Object data;
public PayState(int code, String msg, Object data) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PayState{" +
"[交易状态:]code=" + code +
", [交易详情:]data=" + data +
", msg='" + msg + '\'' +
'}';
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
Payment.class
java
public interface Payment {
// 每次增加一个支付渠道,我们就要去维护这个接口一次
// public final static Payment ALI_PAY = new AliPay();
// public final static Payment JD_PAY = new JDPay();
// public final static Payment WECHAT_PAY = new WeChatPay();
// public final static Payment UNION_PAY = new UnionPay();
PayState pay(String uid, double amount);
}public interface Payment {
// 每次增加一个支付渠道,我们就要去维护这个接口一次
// public final static Payment ALI_PAY = new AliPay();
// public final static Payment JD_PAY = new JDPay();
// public final static Payment WECHAT_PAY = new WeChatPay();
// public final static Payment UNION_PAY = new UnionPay();
PayState pay(String uid, double amount);
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
AliPay.class
java
public class AliPay implements Payment {
public PayState pay(String uid, double amount) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用支付宝");
System.out.println("查询余额,开始扣款");
return new PayState(200,"支付成功",amount);
}
}public class AliPay implements Payment {
public PayState pay(String uid, double amount) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用支付宝");
System.out.println("查询余额,开始扣款");
return new PayState(200,"支付成功",amount);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
JDPay.class
java
public class JDPay implements Payment {
public PayState pay(String uid, double amount) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用京东白条支付");
System.out.println("查询余额,开始扣款");
return new PayState(200,"支付成功",amount);
}
}public class JDPay implements Payment {
public PayState pay(String uid, double amount) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用京东白条支付");
System.out.println("查询余额,开始扣款");
return new PayState(200,"支付成功",amount);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
UnionPay.class
java
public class UnionPay implements Payment {
public PayState pay(String uid, double amount) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用银联卡支付");
System.out.println("查询余额,开始扣款");
return new PayState(200,"支付成功",amount);
}
}public class UnionPay implements Payment {
public PayState pay(String uid, double amount) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用银联卡支付");
System.out.println("查询余额,开始扣款");
return new PayState(200,"支付成功",amount);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
WeChatPay.class
java
public class WeChatPay implements Payment {
public PayState pay(String uid, double amount) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用微信支付");
System.out.println("直接从微信红包扣款");
return new PayState(200,"支付成功",amount);
}
}public class WeChatPay implements Payment {
public PayState pay(String uid, double amount) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用微信支付");
System.out.println("直接从微信红包扣款");
return new PayState(200,"支付成功",amount);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PayType enum
java
public enum PayType {
ALI_PAY(new AliPay()),
JD_PAY(new JDPay()),
WECHAT_PAY(new WeChatPay()),
UNION_PAY(new UnionPay());
private Payment payment;
PayType(Payment payment) {
this.payment = payment;
}
public Payment getPayment() {
return payment;
}
}public enum PayType {
ALI_PAY(new AliPay()),
JD_PAY(new JDPay()),
WECHAT_PAY(new WeChatPay()),
UNION_PAY(new UnionPay());
private Payment payment;
PayType(Payment payment) {
this.payment = payment;
}
public Payment getPayment() {
return payment;
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
PayStrategyTest.class
java
public class PayStrategyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 省略把商品添加到购物车,再从购物车下单
// 直接从订单开始
Order order = new Order("1", "20180311001000009", 324.11);
// 开始支付,选择 微信支付、支付宝、银联卡、京东白条、财付通
// 每个渠道它支付的具体的算法是不一样的
// 基本的算法是固定的
// PayState payState = order.pay(new AliPay());
// PayState payState = order.pay(new JDPay());
// 这个值是在支付的时候才决定用哪个值
PayState payState = order.pay(PayType.ALI_PAY);
System.out.println(payState);
}
}public class PayStrategyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 省略把商品添加到购物车,再从购物车下单
// 直接从订单开始
Order order = new Order("1", "20180311001000009", 324.11);
// 开始支付,选择 微信支付、支付宝、银联卡、京东白条、财付通
// 每个渠道它支付的具体的算法是不一样的
// 基本的算法是固定的
// PayState payState = order.pay(new AliPay());
// PayState payState = order.pay(new JDPay());
// 这个值是在支付的时候才决定用哪个值
PayState payState = order.pay(PayType.ALI_PAY);
System.out.println(payState);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
ComparableTest.class
java
public class ComparableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 这就是一个策略模式
new ArrayList<Object>().sort(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return 0;
}
});
}
}public class ComparableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 这就是一个策略模式
new ArrayList<Object>().sort(new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
return 0;
}
});
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
==assets/Payment策略模式设计的支付的类图.png==
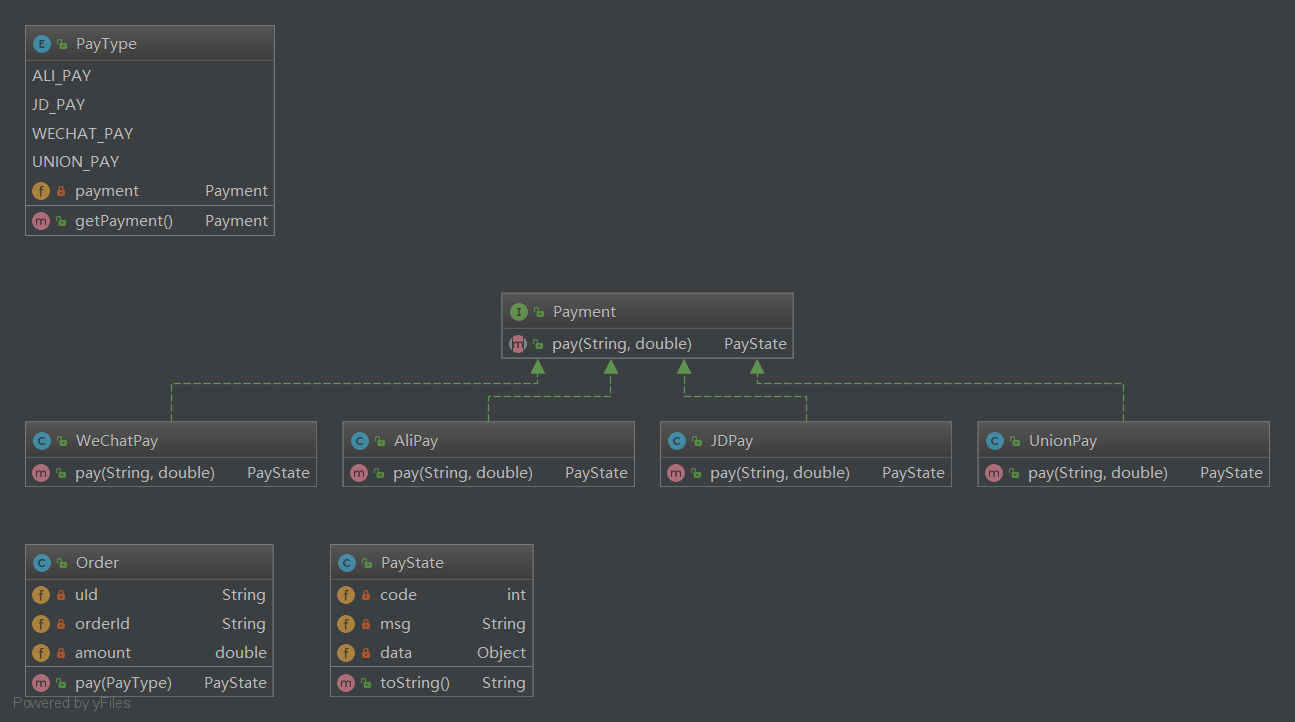
==设计模式都是混合使用,都没有单一存在的。==
用设计模式,是用来解决复杂问题的,把复杂的问题简单化。不要去生搬硬套:容易把简单的事情复杂化。
把简单的事情搞复杂,谁都会,但是把复杂的事情变简单,那需要技术含量(借鉴经验)
一个类,直接 new 一下就好了,为什么要搞个工厂模式呢?
Spring 中的策略模式
BeanFactory
ListableFactory
...Factory
根据用户的配置去选择用什么样的工厂创建出来,这就是==策略模式==,通常会跟抽象==工厂模式==结合使用
举例:爬虫程序
- 根据 URL 来自动选择
BaiDuParser爬取百度的数据SinaParserSougouParser- 返回解析好的 JSON 格式,统一好了
- 保存入库
模板模式:
通常叫做模板方法模式(Template Method)
举例--饮料:
- 加饮料
- 加水
- 烧水
- 加工
- 混合
固定的方法,通常写成抽象方法,让我们自己去实现
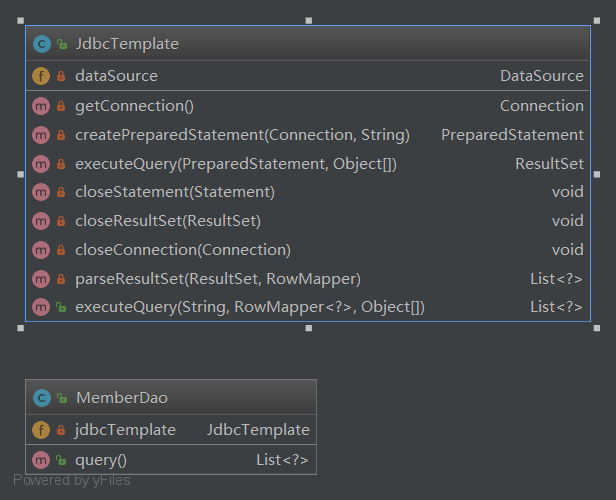
举例--JDBCTemplate
今天利用模板模式,自己写一个
模板模式代码:
Member.class
java
public class Member {
private String userName;
private String passWord;
private int age;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}public class Member {
private String userName;
private String passWord;
private int age;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
JdbcTemplate.class -- 手写 JDBCTemplate
java
public class JdbcTemplate {
private DataSource dataSource;
public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
private Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
return this.dataSource.getConnection();
}
private PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection conn, String sql) throws Exception {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql);
}
private ResultSet executeQuery(PreparedStatement pstmt, Object[] values) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
pstmt.setObject(i, values[i]);
}
return pstmt.executeQuery();
}
private void closeStatement(Statement stmt) throws Exception {
stmt.close();
}
private void closeResultSet(ResultSet rs) throws Exception {
rs.close();
}
private void closeConnection(Connection conn) throws Exception {
// Spring 中,通常是不会关闭,把它放到连接池中回收
}
private List<?> parseResultSet(ResultSet rs, RowMapper rowMapper) throws Exception {
List<Object> result = new ArrayList<Object>();
int rowNum = 1;
while (rs.next()) {
result.add(rowMapper.mapRow(rs, rowNum++));
}
return result;
}
public List<?> executeQuery(String sql, RowMapper<?> rowMapper, Object[] values) {
try {
// 1. 获取链接
Connection conn = this.getConnection();
// 2. 创建语句集
PreparedStatement pstmt = this.createPreparedStatement(conn, sql);
// 3. 执行语句集,并且获得结果集
ResultSet rs = this.executeQuery(pstmt, values);
// 4. 解析语句集
List<?> result = this.parseResultSet(rs, rowMapper);
// 5. 关闭结果集
this.closeResultSet(rs);
// 6. 关闭语句集
this.closeStatement(pstmt);
// 7. 关闭连接
this.closeConnection(conn);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// public abstract Object processResult(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException;
}public class JdbcTemplate {
private DataSource dataSource;
public JdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
private Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
return this.dataSource.getConnection();
}
private PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection conn, String sql) throws Exception {
return conn.prepareStatement(sql);
}
private ResultSet executeQuery(PreparedStatement pstmt, Object[] values) throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
pstmt.setObject(i, values[i]);
}
return pstmt.executeQuery();
}
private void closeStatement(Statement stmt) throws Exception {
stmt.close();
}
private void closeResultSet(ResultSet rs) throws Exception {
rs.close();
}
private void closeConnection(Connection conn) throws Exception {
// Spring 中,通常是不会关闭,把它放到连接池中回收
}
private List<?> parseResultSet(ResultSet rs, RowMapper rowMapper) throws Exception {
List<Object> result = new ArrayList<Object>();
int rowNum = 1;
while (rs.next()) {
result.add(rowMapper.mapRow(rs, rowNum++));
}
return result;
}
public List<?> executeQuery(String sql, RowMapper<?> rowMapper, Object[] values) {
try {
// 1. 获取链接
Connection conn = this.getConnection();
// 2. 创建语句集
PreparedStatement pstmt = this.createPreparedStatement(conn, sql);
// 3. 执行语句集,并且获得结果集
ResultSet rs = this.executeQuery(pstmt, values);
// 4. 解析语句集
List<?> result = this.parseResultSet(rs, rowMapper);
// 5. 关闭结果集
this.closeResultSet(rs);
// 6. 关闭语句集
this.closeStatement(pstmt);
// 7. 关闭连接
this.closeConnection(conn);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// public abstract Object processResult(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException;
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
RowMapper<T>.class
java
public interface RowMapper<T> {
public T mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws Exception;
}public interface RowMapper<T> {
public T mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws Exception;
}1
2
3
2
3
MemberDao.class
java
/**
* 解耦
* 抽象类 >>>>>>>> 实现接口
* <br>Darian
**/
public class MemberDao {
// 为什么不继承,主要是为了解耦
// 类似于静态代理,静态代理 JDBCTemplate 的一些方法
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(null);
public List<?> query() {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_member";
return jdbcTemplate.executeQuery(sql, new RowMapper<Object>() {
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws Exception {
Member member = new Member();
member.setUserName(rs.getString("userName"));
member.setPassWord(rs.getString("passWord"));
member.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
return member;
}
}, null);
}
}/**
* 解耦
* 抽象类 >>>>>>>> 实现接口
* <br>Darian
**/
public class MemberDao {
// 为什么不继承,主要是为了解耦
// 类似于静态代理,静态代理 JDBCTemplate 的一些方法
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(null);
public List<?> query() {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_member";
return jdbcTemplate.executeQuery(sql, new RowMapper<Object>() {
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws Exception {
Member member = new Member();
member.setUserName(rs.getString("userName"));
member.setPassWord(rs.getString("passWord"));
member.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
return member;
}
}, null);
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
MemberDaoTest.class
java
public class MemberDaoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDao();
memberDao.query();
}
}public class MemberDaoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MemberDao memberDao = new MemberDao();
memberDao.query();
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
==assets/JdbcTemplate-手写JDBC模板模式类图.png==
==assets/模板模式-旅游路线规划.png==
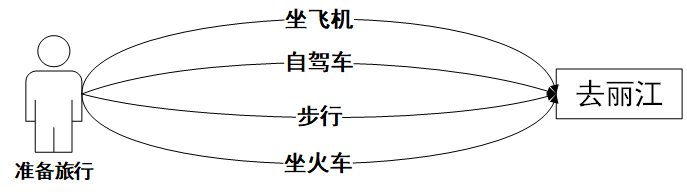
策略模式和模板模式对比
策略模式
- 只有选择权(由用户选择已有的固定算法)
模板模式
侧重点不是选择,你没得选择,你必须这么做,你可以参与某一部分内容的自定义去改变执行结果,没办法改变执行流程。
